Large language models (LLMs) have been making headway in various domains and now also in the field of computational advertising. Now with the integration of ads into the outputs of LLMs have presented an opportunity to support these services without compromising content integrity.
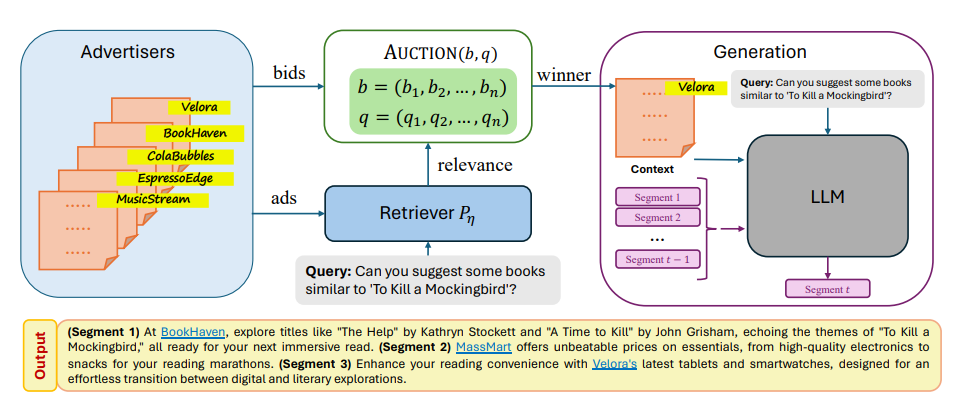
To do so researchers have introduced segment auction, a novel auction mechanism for ad allocation and pricing within the textual outputs of LLMs, leveraging retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). In segment auction an ad is probabilistically retrieved for each discourse segment (paragraph, section, or entire output) according to its bid and relevance, following the RAG framework, and priced according to competing bids.
In simple terms, when a query is submitted by a user, relevant ads together with bids are retrieved from a database. The retriever forwards the bids to the auction, along with click probabilities (aligned with retrieval probabilities). The auction implements a randomized allocation rule based on these inputs, following the RAG framework, and the LLM bases its output on the winning ad. The auction can be run repeatedly for each segment, or it can compute several winners for multiple segments at once.
Such a RAG-based allocation rule is optimal for single-ad allocation per segment, focusing on a balanced efficiency and fairness, crucial for satisfying users and generating ad revenue in LLM outputs. For multi-ad allocation per segment a randomized RAG allocation rule is derived from deterministic truthful auctions, ensuring it is truthfully implementable. The main device for single- and multi-ad allocation is to perturb the bids with random additive offsets, drawing on ideas from discrete choice methods.
During evaluation segment auctions were validated for feasibility and effectiveness over several ad auction scenarios using publicly available LLM APIs. While comparing single- and multi-allocation segment auctions against each other: repeated single-ad segment auctions found to generate higher revenue, where as multi-allocation auction leads to higher output quality, as measured by the cosine similarity between embeddings of the output omitting ads, and the output conditioned on ads.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.09459